Provisioning Cloud Infrastructure using AWS CloudFormation Templates
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a secure cloud services platform, offering compute power, database storage, content delivery, and other functionalities to help businesses scale and grow.
It gives organizations a secure and robust platform to develop their custom cloud-based solutions and has several unique features that make it one of the most reliable and flexible cloud platform such as
- Mobile-friendly access through AWS Mobile Hub and AWS Mobile SDK
- Fully managed purpose-built Databases
- Serverless cloud functions
- Range of storage options that are affordable and scalable.
- Unbeatable security and compliance
Following are some core services offered by AWS:
AWS Core services
- An EC2 instance is a virtual server in Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for running applications on the AWS infrastructure.
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a cloud-based block storage system provided by AWS that is best used for storing persistent data.
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables us to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that we have defined. This virtual network closely resembles a traditional network that we would operate in our own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
- Amazon S3 or Amazon Simple Storage Service is a service offered by Amazon Web Services that provides object storage through a web service interface. Amazon S3 uses the same scalable storage infrastructure that Amazon.com uses to run its global e-commerce network.
- AWS security groups (SGs) are associated with EC2 instances and provide security at the protocol and port access level. Each security group — working much the same way as a firewall — contains a set of rules that filter traffic coming into and out of an EC2 instance.
Let us look more deeply at one of AWS’s core services – AWS CloudFormation – that is key for managing workloads on AWS.
1. CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is a service that helps us model and set up our Amazon Web Services resources so that we can spend less time managing those resources and more time focusing on our applications that run in AWS. We create a template that describes all the AWS resources that we want (like Amazon EC2 instances or S3 buckets), and AWS CloudFormation takes care of provisioning and configuring those resources for us. We don’t need to individually create and configure AWS resources and figure out what’s dependent on what; AWS CloudFormation handles all of that.
A stack is a collection of AWS resources that you can manage as a single unit. In other words, we can create, update, or delete a collection of resources by creating, updating, or deleting stacks. All the resources in a stack are defined by the stack’s AWS CloudFormation template.
2. CloudFormation template
CloudFormation templates can be written in either JSON or YAML. The structure of the template in YAML is given below:
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "version date"
Description:
String
Metadata:
template metadata
Parameters:
set of parameters
Mappings:
set of mappings
Conditions:
set of conditions
Resources:
set of resources
Outputs:
set of outputsIn the above yaml file,
- AWSTemplateFormatVersion – The AWS CloudFormation template version that the template conforms to.
- Description – A text string that describes the template.
- Metadata – Objects that provide additional information about the template.
- Parameters – Values to pass to our template at runtime (when we create or update a stack). We can refer to parameters from the Resources and Outputs sections of the template.
- Mappings – A mapping of keys and associated values that we can use to specify conditional parameter values, like a lookup table. We can match a key to a corresponding value by using the Fn::FindInMap intrinsic function in the Resources and Outputs sections.
- Conditions – Conditions that control whether certain resources are created or whether certain resource properties are assigned a value during stack creation or update. For example, we can conditionally create a resource that depends on whether the stack is for a production or test environment.
- Resources – Specifies the stack resources and their properties, such as an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud instance or an Amazon Simple Storage Service bucket. We can refer to resources in the Resources and Outputs sections of the template.
- Outputs – Describes the values that are returned whenever we view our stack’s properties. For example, we can declare an output for an S3 bucket name and then call the AWS cloudformation describe-stacks AWS CLI command to view the name.
Resources is the only required section in the CloudFormation template. All other sections are optional.
3. CloudFormation template to create S3 bucket
S3template.yml
Resources:
HelloBucket:
Type: AWS::S3::BucketIn AWS Console, go to CloudFormation and click on Create Stack
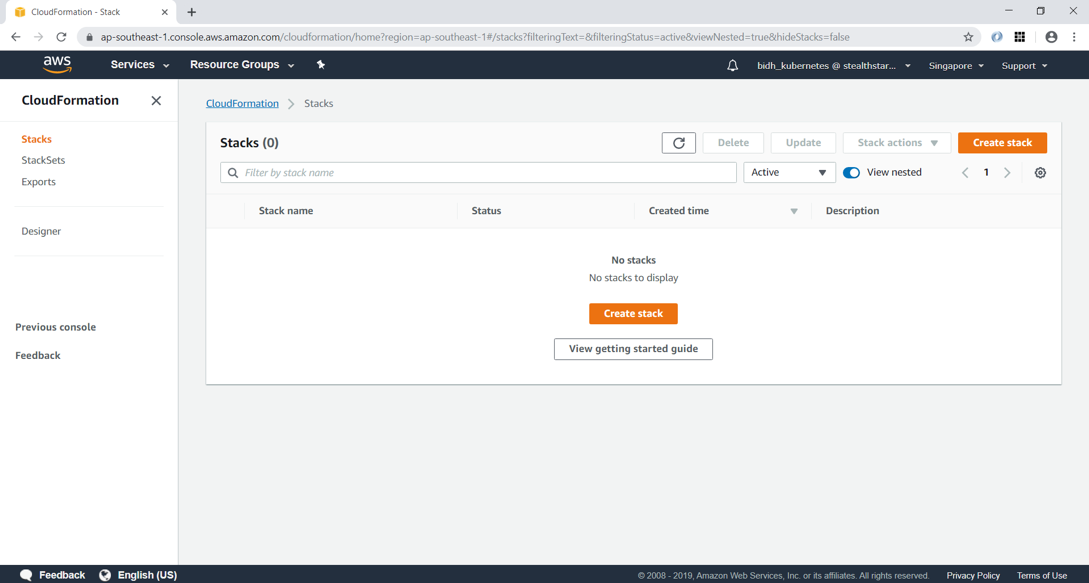
Upload the template file which we created. This will get stored in an S3 location, as shown below.
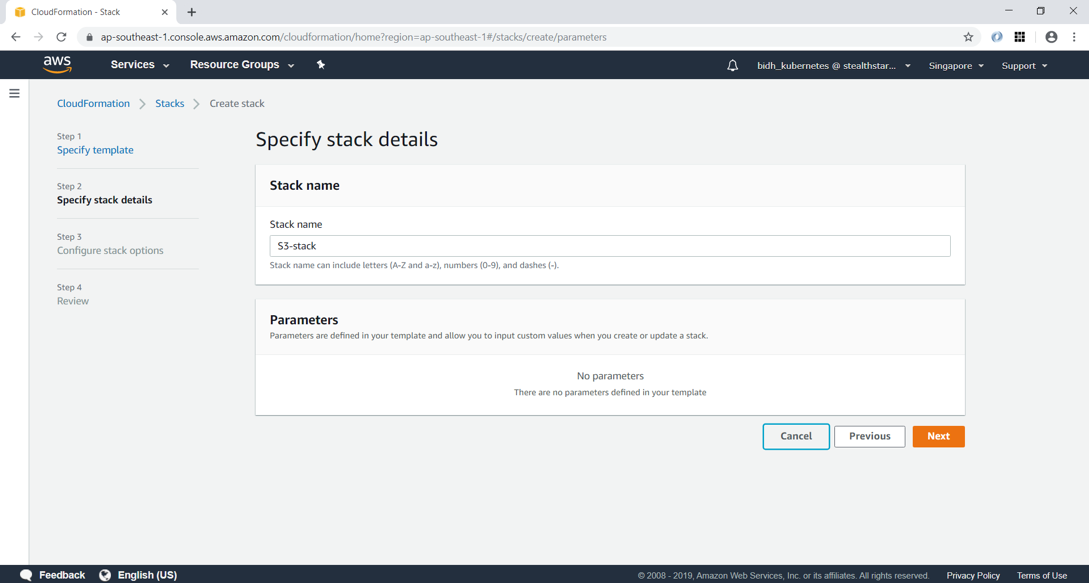
Click next and give a stack name
Click Next and then “Create stack”. After a few minutes, you can see that the stack creation is completed.
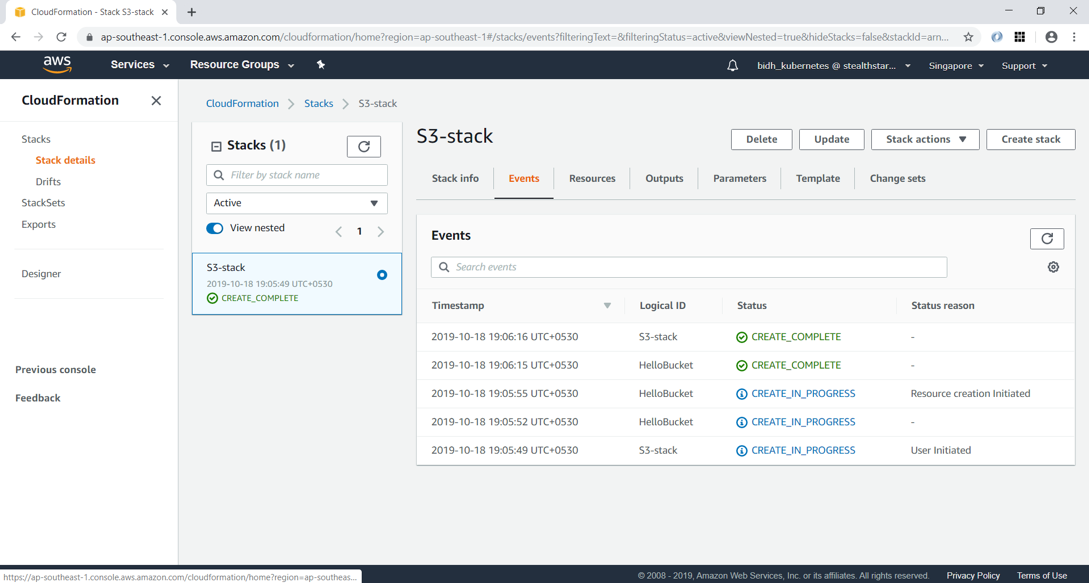
Clicking on the Resource tab, you can see that the S3 bucket has been created with name “s3-stack-hellobucket-buhpx7oucrgn”. AWS has provided this same since we didn’t specify the BucketName property in YAML.

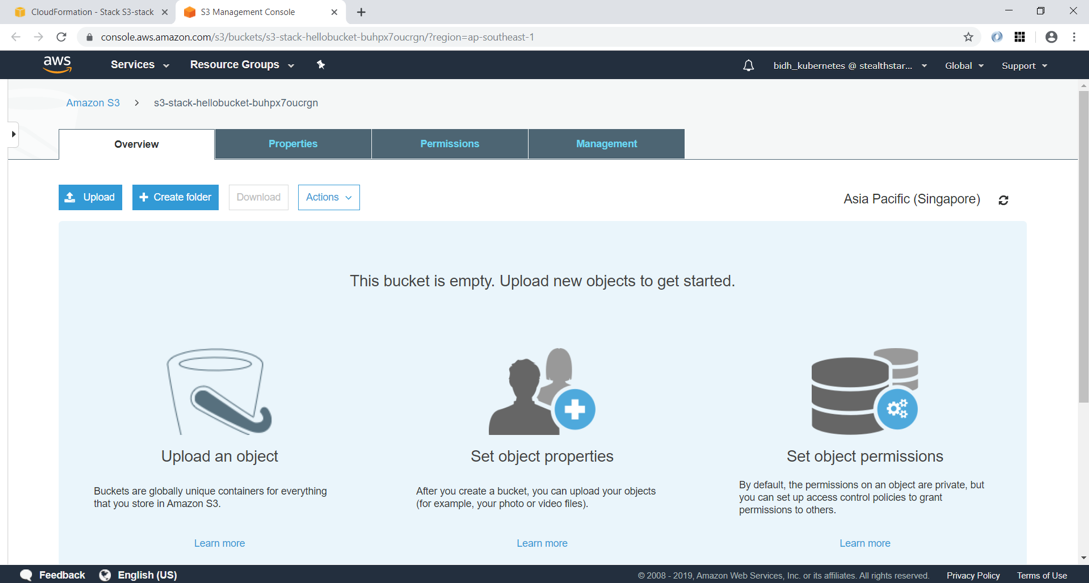
Note that deleting the stack will delete the S3 bucket which it had created.
4. Intrinsic functions
AWS CloudFormation provides several built-in functions that help you manage your stacks.
In the below example, we create two resources – a Security Group and an EC2 Instance, which uses this Security Group. We can refer to the Security Group resource using the !Ref function.
Ec2template.yml
Resources:
Ec2Instance:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::Instance'
Properties:
SecurityGroups:
- !Ref InstanceSecurityGroup
KeyName: mykey
ImageId: ''
InstanceSecurityGroup:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup'
Properties:
GroupDescription: Enable SSH access via port 22
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: '22'
ToPort: '22'
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0Some other commonly used intrinsic functions are
- Fn::GetAtt – returns the value of an attribute from a resource in the template.
- Fn::Join – appends a set of values into a single value, separated by the specified delimiter. If a delimiter is an empty string, the set of values are concatenated with no delimiter.
- Fn::Sub – substitutes variables in an input string with values that you specify. In our templates, we can use this function to construct commands or outputs that include values that aren’t available until we create or update a stack.
5. Parameters
Parameters enable us to input custom values to your template each time you create or update a stack.
TemplateWithParameters.yaml
Parameters:
InstanceTypeParameter:
Type: String
Default: t2.micro
AllowedValues:
- t2.micro
- m1.small
- m1.large
Description: Enter t2.micro, m1.small, or m1.large. Default is t2.micro.
Resources:
Ec2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
InstanceType:
Ref: InstanceTypeParameter
ImageId: ami-0ff8a91507f77f867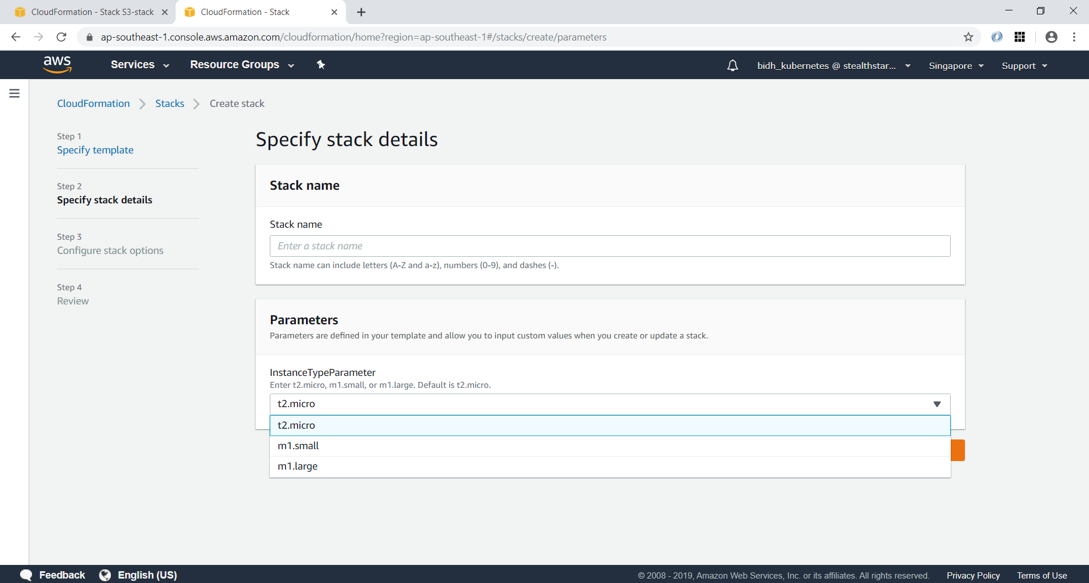
6. Pseudo Parameters
Pseudo parameters are parameters that are predefined by AWS CloudFormation. We do not declare them in our template. Use them the same way as we would a parameter as the argument for the Ref function.
Commonly used pseudo parameters:
- AWS: Region – Returns a string representing the AWS Region in which the encompassing resource is being created, such as us-west-2
- AWS::StackName – Returns the name of the stack as specified during cloudformation create-stack, such as teststack
7. Mappings
The optional Mappings section matches a key to a corresponding set of named values. For example, if you want to set values based on a region, we can create a mapping that uses the region name as a key and contains the values we want to specify for each specific region. We use the Fn::FindInMap intrinsic function to retrieve values in a map.
We cannot include parameters, pseudo parameters, or intrinsic functions in the Mappings section.
TemplateWithMappings.yaml
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Mappings:
RegionMap:
us-east-1:
HVM64: ami-0ff8a91507f77f867
HVMG2: ami-0a584ac55a7631c0c
us-west-1:
HVM64: ami-0bdb828fd58c52235
HVMG2: ami-066ee5fd4a9ef77f1
eu-west-1:
HVM64: ami-047bb4163c506cd98
HVMG2: ami-0a7c483d527806435
ap-northeast-1:
HVM64: ami-06cd52961ce9f0d85
HVMG2: ami-053cdd503598e4a9d
ap-southeast-1:
HVM64: ami-08569b978cc4dfa10
HVMG2: ami-0be9df32ae9f92309
Resources:
myEC2Instance:
Type: "AWS::EC2::Instance"
Properties:
ImageId: !FindInMap [RegionMap, !Ref "AWS::Region", HVM64]
InstanceType: m1.small8. Outputs
The optional Outputs section declares output values that we can import into other stacks (to create cross-stack references), return in response (to describe stack calls), or view on the AWS CloudFormation console. For example, we can output the S3 bucket name for a stack to make the bucket easier to find.
In the below example, the output named StackVPC returns the ID of a VPC, and then exports the value for cross-stack referencing with the name VPCID appended to the stack’s name.
Outputs:
StackVPC:
Description: The ID of the VPC
Value: !Ref MyVPC
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}-VPCID"Share this:

CloudIQ is a leading Cloud Consulting and Solutions firm that helps businesses solve today’s problems and plan the enterprise of tomorrow by integrating intelligent cloud solutions. We help you leverage the technologies that make your people more productive, your infrastructure more intelligent, and your business more profitable.
LATEST THINKING
INDIA
Chennai One IT SEZ,
Module No:5-C, Phase ll, 2nd Floor, North Block, Pallavaram-Thoraipakkam 200 ft road, Thoraipakkam, Chennai – 600097
© 2023 CloudIQ Technologies. All rights reserved.

