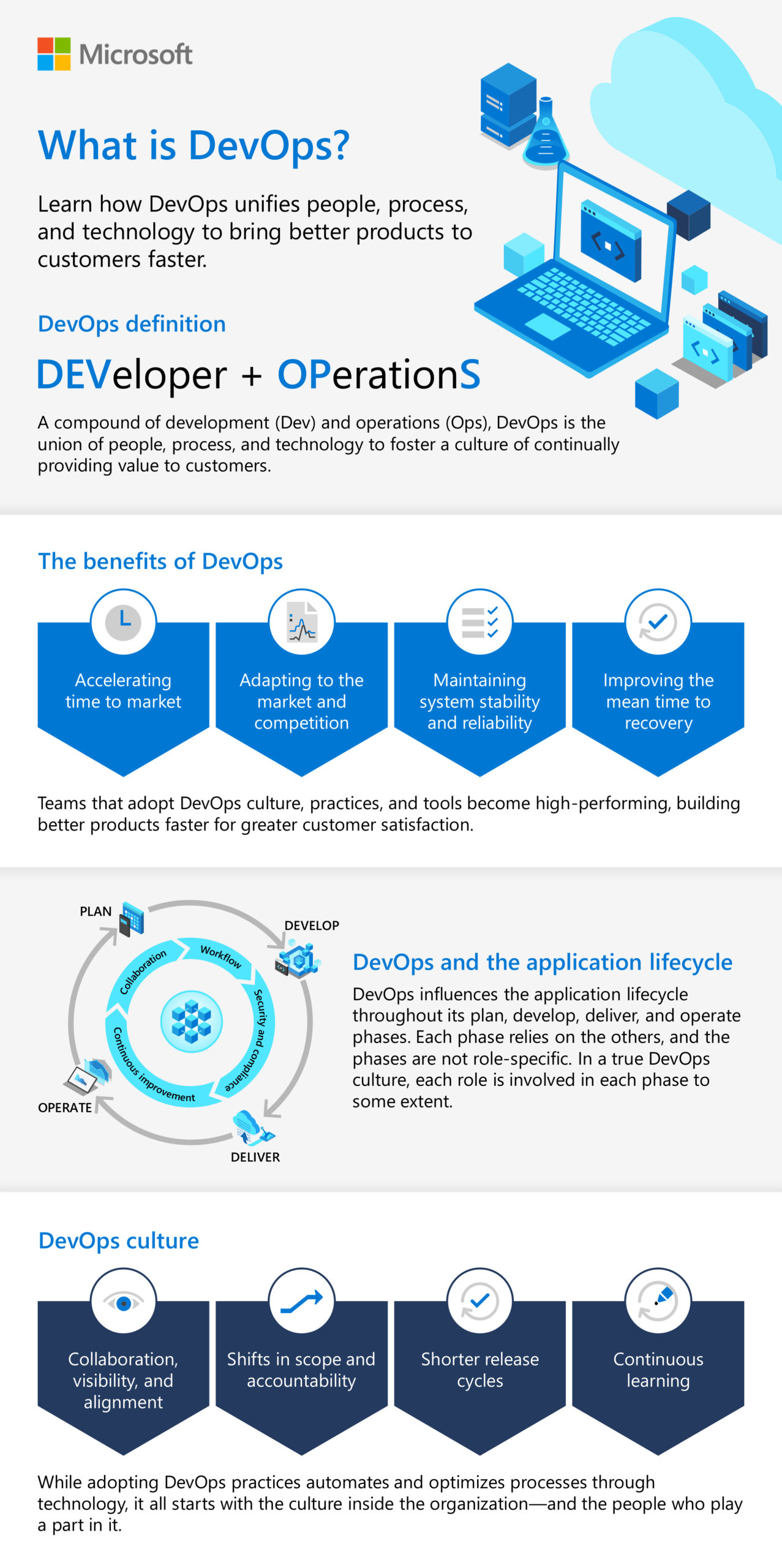
A microservices-based architecture introduces agility, flexibility and supports a sustainable DEVOPS culture ensuring closer collaboration within businesses and the news is that it’s actually happening for those who embraced it.
True, monolith apps architectures have enabled businesses to benefit from IT all along as it is single coded, simple to develop, test and run. As they are also based on a logical modular hexagonal or layered architectures (Presentation Layer responsible for handling HTTP requests and responding with either HTML or JSON/XML, Business logic layer, Database access and Apps integration) they cover and tie all processes, functions and gaps to an extent.
Despite these ground level facts, monolith software, which is instrumental for businesses embrace IT in their initial stages and which even exists today, is seeing problems. The growing complex business operation conditions are purely to be blamed.
So, how do businesses today address new pressures caused by digitization, continuous technology disruptions, increased customer awareness & interceptions and sudden regulatory interventions? The answer lies in agility, flexibility and scalability of the underlying IT infrastructure- the pillars of rapid adaptability to changes.
Monolith Apps, even though it is based on a well-designed 3 tier architecture, in the long run, loses fluidity and turns rigid. Irrespective of its modularity, modules are still dependent on each other and any minimal change in one module needs generation and deployment of all artifacts in each server pool, touched across the distributed environment.
Besides whenever there is a critical problem, the blame game starts amongst the UI developers, business logic experts, backend developers, database programmers, etc as they are predominantly experts in their domains, but have little knowledge about other processes. As the complexity of business operations sets in, the agility, flexibility and scalability part of your software is highly tested in a monolithic environment.
Here’s where Microservices plays a huge role as the underlying architecture helps you break your software applications into independent loosely coupled services that can be deployed and managed solely at that level and needn’t have to depend on other services.
For example, if your project needs you to design and manage inventory, sales, shipping, and billing and UI shopping cart modules, you can break each service down as an independently deployable module. Each has its own database, where monitoring and maintenance of application servers are done independently as the architecture allows you to decentralize the database, reducing complexity. Besides it enables continuous delivery/deployment of large, complex applications which means technology also evolves along with the business.
The other important aspect is that microservices promotes a culture wherein whoever develops the service is also responsible to manage it. This avoids the handover concept and the following misunderstandings and conflicts whenever there is a crisis.
In line with the DevOps concept, Microservices enables easy collaboration between the development and operations team as they embrace and work on a common toolset that establishes common terminology, as well as processes for requirements, dependencies, and problems. There is no denying the fact that DevOps and microservices work better when applied together.
Perhaps that’s the reason companies like Netflix, Amazon, etc are embracing the concept of microservices in their products. And for other new businesses embracing it, a new environment where agility, flexibility and closer collaboration between business and technology becomes a reality providing the much-needed edge in these challenging times.